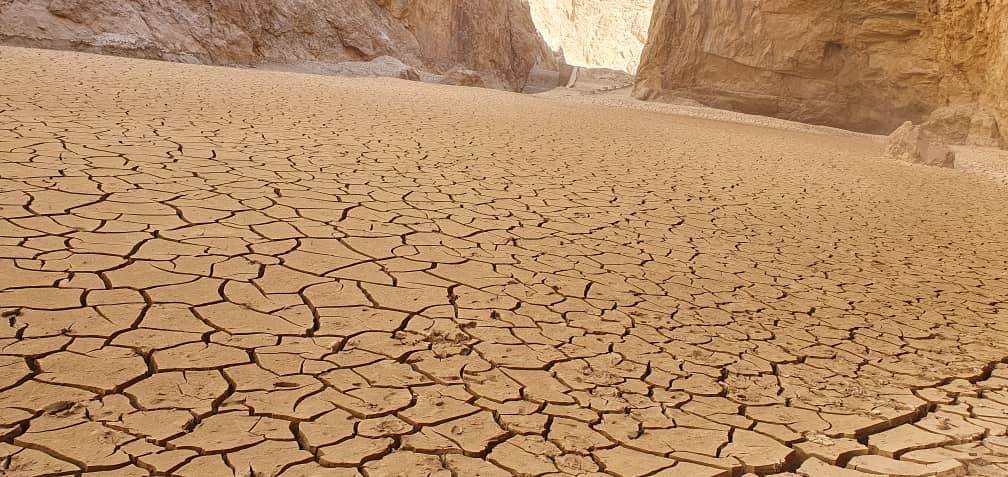
Climate changes

Here are several strategies PGEO could implement to address the negative impacts of climate change in Bamyan, focusing on both immediate and long-term solutions:
1. Sustainable Agricultural Practices
- Climate-Resilient Crops: Introduce and promote the use of drought-resistant and climate-resilient crop varieties, helping farmers maintain productivity in changing weather conditions.
- Water Conservation Techniques: Use methods such as rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation to maximize water efficiency. This is critical in areas facing reduced rainfall and water shortages.
- Soil Conservation: Educate farmers on techniques like crop rotation, cover cropping, and agroforestry to prevent soil erosion, maintain soil fertility, and enhance water retention.
- Greenhouse Farming: Implement greenhouse projects to allow year-round farming and protect crops from harsh weather conditions.
2. Community-Based Water Management
- Water Resource Mapping: Collaborate with local communities to map and monitor water resources. This can help in understanding water availability and demand, ensuring equitable distribution during times of scarcity.
- Rehabilitation of Water Infrastructure: Rehabilitate irrigation systems, wells, and water storage facilities to ensure a sustainable water supply for agriculture and domestic use.
- Watershed Management Programs: Engage in watershed management to restore and maintain water catchment areas, which are vital for sustaining both agriculture and drinking water.
3. Renewable Energy Integration
- Solar-Powered Irrigation: Introduce solar-powered pumps for irrigation, reducing dependency on fossil fuels and providing a sustainable solution for water management.
- Energy-Efficient Technologies: Encourage the use of energy-efficient technologies in farming, food processing, and storage, reducing carbon footprints while improving productivity.
- Renewable Energy Initiatives: Expand the use of renewable energy sources like solar and wind to power homes and community buildings, which can reduce deforestation for fuel and alleviate energy poverty.
4. Disaster Risk Reduction and Preparedness
- Early Warning Systems: Develop and deploy climate-related early warning systems that provide farmers and communities with timely information on extreme weather events, such as floods or droughts, to help them take preventive actions.
- Disaster Preparedness Training: Provide communities with training on disaster preparedness, including evacuation plans and first aid training to enhance resilience during climate-induced crises.
- Climate-Resilient Infrastructure: Invest in climate-resilient infrastructure, such as flood defenses, roads, and storage facilities, to minimize damage from extreme weather events.
5. Community Engagement and Capacity Building
- Training and Education: Conduct workshops and training sessions on climate change adaptation strategies, sustainable farming techniques, and disaster preparedness. This will empower farmers and local communities to adapt to the changing climate.
- Women and Youth Involvement: Engage women and youth in climate action initiatives, recognizing their roles as key actors in community development. Encourage their participation in decision-making processes related to agriculture and resource management.
- Community-Based Monitoring: Establish community-based monitoring groups to assess and report on climate impacts, ensuring timely interventions and fostering local ownership of solutions.
6. Reforestation and Ecosystem Restoration
- Tree Planting Campaigns: Initiate reforestation and afforestation programs to combat desertification and improve water retention. Trees help restore degraded land and provide a buffer against extreme temperatures and soil erosion.
- Conservation of Local Ecosystems: Promote the protection and rehabilitation of natural ecosystems, such as wetlands and forests, which play a crucial role in regulating the local climate and water cycles.
7. Advocacy and Policy Engagement
- Policy Influence: Advocate for stronger local and national policies on climate change, disaster risk management, and sustainable agriculture. Collaborate with the government and other stakeholders to ensure that climate adaptation and resilience-building efforts are integrated into development plans.
- Funding and Partnerships: Seek partnerships with international organizations, governments, and donors to fund and support climate resilience projects in Bamyan. This could include grants for renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and water resource management.
8. Research and Innovation
- Research on Local Climate Impacts: Conduct or collaborate on research to understand the specific impacts of climate change in Bamyan, enabling the development of tailored interventions that address local vulnerabilities.
- Pilot Projects: Implement pilot projects in climate-sensitive areas to test new approaches in water conservation, agriculture, and disaster resilience. Successful models can be scaled up and applied across other regions of Afghanistan.
By implementing these strategies, PGEO can enhance the resilience of communities in Bamyan, ensuring they are better prepared to cope with the adverse effects of climate change while fostering sustainable development.
Also to address the negative impacts of climate change in Bamyan, Afghanistan, PGEO can adopt a comprehensive set of strategies to build resilience and promote sustainable development in the region:
- Sustainable Agriculture Practices:
- Drought-Resistant Crops: Introduce and promote the cultivation of drought-resistant and heat-tolerant crop varieties to mitigate the impact of irregular rainfall and rising temperatures.
- Agroforestry: Encourage integrating trees with crops, as trees can help retain soil moisture, reduce erosion, and provide additional income through fruit or timber production.
- Water-Efficient Irrigation Systems: Implement drip irrigation and other water-saving technologies to conserve limited water resources, ensuring that agriculture remains viable during periods of drought.
- Capacity Building and Training:
- Farmer Training Programs: Offer regular workshops to train local farmers in sustainable agricultural practices, climate-resilient farming techniques, and the use of modern tools and technologies to increase productivity under adverse conditions.
- Climate Change Awareness Campaigns: Raise awareness about the effects of climate change on local ecosystems, water resources, and agriculture through public education initiatives. This will enable communities to take proactive measures to mitigate its impact.
- Ecosystem Restoration and Conservation:
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Implement reforestation programs to restore degraded lands and protect water catchment areas, helping to prevent soil erosion and floods while increasing carbon sequestration.
- Protecting Biodiversity: Promote the conservation of native plant species and natural habitats to preserve biodiversity, which can provide ecosystem services like pollination, pest control, and water purification.
- Alternative Livelihoods:
- Diversification of Income: Encourage the diversification of livelihoods by promoting non-agricultural activities such as handicrafts, eco-tourism, and renewable energy-based businesses to reduce reliance on farming, which is heavily impacted by climate change.
- Microfinance and Support for Entrepreneurs: Provide financial support and resources for small-scale entrepreneurs to start new businesses, particularly in areas like renewable energy, that are less vulnerable to climate risks.
- Climate-Resilient Infrastructure Development:
- Flood and Drought Protection Measures: Build and maintain protective structures like levees, reservoirs, and check dams to mitigate the effects of extreme weather events such as floods and droughts.
- Energy Infrastructure: Promote the use of solar and other renewable energy sources to reduce dependency on fossil fuels and ensure energy access even in remote areas.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Preparedness:
- Early Warning Systems: Establish a climate hazard early warning system to alert communities in advance of extreme weather events like floods and droughts, allowing them to take preventive measures.
- Disaster Response Training: Train local communities and volunteers in disaster response and recovery, enabling them to respond effectively during emergencies.
- Policy Advocacy and Collaboration:
- Partnerships with Government and NGOs: Collaborate with local, national, and international organizations to develop policies and programs that prioritize climate adaptation and mitigation.
- Influencing Policy: Advocate for climate-resilient policies at the local and national levels, particularly in sectors like agriculture, water management, and disaster preparedness.
By implementing these strategies, PGEO can help Bamyan’s communities become more resilient to the effects of climate change while fostering sustainable development and ensuring the well-being of its residents.